Predicting such extreme financial events as market crashes, bank failures, and currency crises is of great importance to investors and policy markers because they destabilize the financial system and can greatly shrink asset value. A number of different models have been developed to predict the occurrence of financial distresses. Here, an early warning model is built to predict the recurrence of financial extremes based on the distribution of recurrence intervals between consecutive historical extremes. The extreme returns are determined according to quantile thresholds which includes 95%, 97.5%, and 99%. By taking into consideration the time in which extremes occur, our prediction of extreme returns is based on the hazard probability
W(Δ
t|
t), which measures the probability that following an extreme return occurring at
t time in the past there is an additional waiting time Δ
t before another extreme return occurs, where the hazard probability
W(Δ
t|
t)=
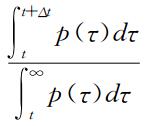
. In this paper, three common functions are employed to fit the recurrence interval distributions, and it is found that the recurrence intervals follow
q-exponential distribution. Using the hazard probability, an extreme-return-prediction model is developed for forecasting imminent financial extreme events. When the hazard probability is greater than the hazard threshold, this model can warn when an extreme event is about to occur. The hazard threshold is obtained by maximizing the usefulness of extreme forecasts. In order to test the validity of our extreme-return-prediction model, a recurrence interval analysis of financial extremes in the Shanghai Composite Index during the period from 1990 to 2016 is performed. The data before each turbulent period are used to calibrate the model and each turbulent period that follows for out-of-sample forecasting, which obtains three in-sample periods:2000-2002,2006-2009 and 2014-2016. It is found that the recurrence intervals exhibit the characteristics of positive skewness, fat-tailed distributions, and positive autocorrelations. Both in-sample and out-of-sample tests indicate that our model has great predicting power. Two trading strategies, including a long strategy and a short strategy, are further designed to check whether our model is able to provide significant profits. When the extreme positive return is greater than the threshold, a buying signal is gotten. When the hazard probability is less than the positive threshold after Δ
t time, a selling signal will occur, which is defined as a long strategy. For the extreme negative return, a short strategy is also defined. In addition to the Shanghai Composite Index, four stock indexes of CAC40, FTSE, HIS and N225 are also researched. The back tests reveal that the two trading strategies can efficiently avoid the decline stage, and the long strategy earn higher profits.


